Cell free DNA in maternal blood
Interpretation of results
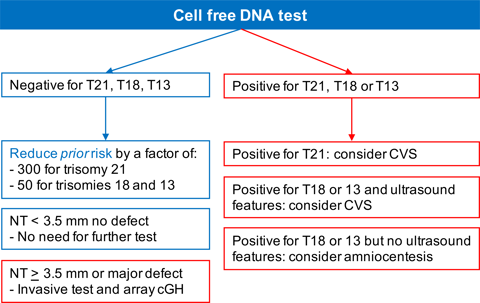
The cfDNA test is a screening rather than a diagnostic test. The results are given in terms of risk, with the majority of companies reporting results for each chromosome as low-risk (usually less than 1 in 10,000) or high-risk (more than 99%).
A positive or high-risk cfDNA result should be confirmed by invasive testing.
- In the case of first-trimester screening and positive cfDNA result for trisomy 21 the diagnostic test can be CVS.
- In the case of trisomies 18 and 13 a positive result should be followed by a detailed ultrasound examination and if the characteristic defects associated with these trisomies are detected then CVS can be carried out; if no defects are detected in the scan the preferred diagnostic test is amniocentesis to avoid an erroneous result due to placenta confined mosaicism.
A negative or low-risk cfDNA result is reassuring that the fetus is unlikely to be affected by the trisomy under investigation.
- The prior risk (based on maternal age or the results of a prior method of screening) can be reduced by a factor of about 300 for trisomy 21 and 50 for trisomies 18 and 13.