Cell free DNA in maternal blood
Screening for chromosomal abnormalities
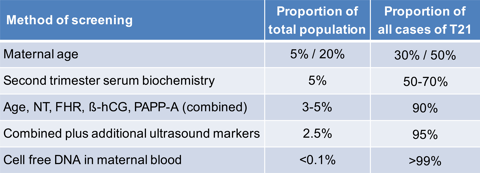
Analysis of cfDNA in maternal blood can detect about 99% of fetuses with trisomy 21 and 98% of fetuses with trisomies 18 or 13 at a false positive rate (FPR) of 0.1-0.2%. Therefore, in singleton pregnancies the performance of screening for these trisomies by cfDNA testing is superior, both in terms of higher detection rate and substantially lower FPR, to that of all other methods combining maternal age, first- or second-trimester ultrasound findings and first- or second-trimester serum biochemical analysis.
- In twin pregnancies performance of screening for trisomy 21 is encouraging but the number of cases reported is small.
- This method can also be used to screen for sex-chromosome aneuploidies and certain microdeletions, such as 22q11 (Di George syndrome). There are insufficient data for accurate assessment of performance of screening for these conditions.