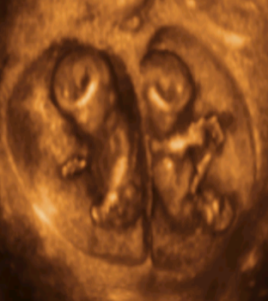
Twin pregnancies
Twins account for 1-2% of all pregnancies with two-thirds being dizygotic (non-identical) and one-third monozygotic (identical).
- The prevalence of dizygotic twins is higher in Black than White women, increases with maternal age and method of conception (20% with ovulation induction).
- The prevalence of monozygotic twins is similar in all ethnic groups and does not vary with maternal age but may be 2-3 times higher following in-vitro fertilisation procedures.
- In the last 20 years the rate of twinning has increased. This increase is most marked for dizygotic twins. Two-thirds of the increase in twins is due to the use of assisted reproduction techniques and one-third due to increasing maternal age.
- In dizygotic twins each fetus has its own placenta and amniotic sac. In monozygotic pregnancies, there may be sharing of the same placenta (monochorionic), amniotic sac (monoamniotic) or even fetal organs (conjoined or Siamese). One-third of monozygotic twins are dichorionic (DC) and two-thirds are monochorionic (MC).
- Therefore, all MC twins are monozygotic and 6 out of 7 DC twins are dizygotic.