Second trimester scan
Minor abnormalities
Minor fetal abnormalities or soft markers are common and they are not usually associated with any handicap, unless there is an underlying chromosomal defect.
- Invasive testing of all pregnancies with these markers would have major implications, both in terms of miscarriage and in economic costs. It is best to base counseling on an individual estimated risk for a chromosomal defect, rather than the arbitrary advice that invasive testing is recommended because the risk is ‘high’.
- The estimated risk can be derived by multiplying the a priori risk (based on the results of previous screening) by the likelihood ratio of the specific abnormality or marker.
For isolated abnormalities the likelihood ratio for trisomy 21 is:
- About 1 (therefore the a priori risk is not increased) in the case of choroid plexus cysts, echogenic endocardiac focii, mild hydronephrosis and short femur.
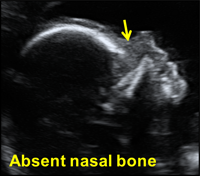
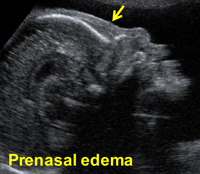
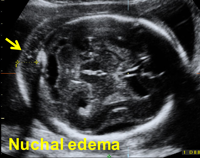
- About 10 (therefore there is a 10-fold increase in the a priori risk) for nuchal or prenasal edema and hypoplastic nasal bone.