Fetal growth restriction
Monitoring
Monitoring interval: This should be inversely related to the severity of fetal compromize and the speed of deterioration in the clinical condition. Worsening in the fetal condition is suggested by:
- Oligohydramnios
- Middle cerebral artery: Decrease in pulsatility index (PI)
- Umbilical artery: Increase in PI, absent or reversed end-diastolic flow
- Ductus venosus: Increase in PI, absent or reversed a-wave
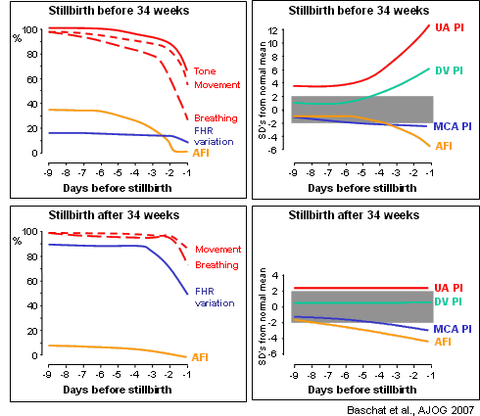
Changes preceeding stillbirth: Serial assessments in pregnancies resulting in stillbirth have demonstrated major differences in the responses during the last three days preceeding death depending on gestation:
- In stillbirths before 34 weeks there is a major increase in the umbilical artery and ductus venosus PI and decrease in amniotic fluid volume and fetal tone and movements. The intensity of monitoring should increase if there is worsening in umbilical artery and/or ductus venosus PI or decrease in amniotic fluid volume and may vary from once per week to daily
- In stillbirths after 34 weeks there is a decrease in middle cerebral artery PI fetal heart rate variation and amniotic fluid volume. Special attention should be placed on the middle cerebral artery PI and delivery should be considered if this decreases, even if the value remains above the 5th centile